- Course Materials Che 31. Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution Manual
- Course Materialsche 31. Introduction To Chemical Engineering
Specializations in Chemical and Molecular Engineering Chemical and Molecular Engineering students may choose from one of the eight specializations offered or, with the approval of a program director, create a custom specialization. Each specialization requires the completion of three technical elective courses at the 300-level or higher. Chemical engineering encompasses the translation of molecular information into discovery of new products and processes. It involves molecular transformations—chemical, physical, and biological—with multi-scale description from the submolecular to the macroscopic, and the analysis and synthesis of such systems.
Unformatted text preview: CHE 31.Introduction to Chemical Engineering Problem Set 1.Fundamental Concepts in Chemical Engineering Calculations (Problems adopted from Elementary Principles of Chemical Process by Felder & Rousseau and Basic Principles and Calculations in Chemical Engineering by Himmelblau and Briggs) 1. Introduction to Chemical Engineering Calculations(Credit: 3 Units) The course is intended to provide students a clear overview of the field of chemical engineering and introduce them to the elementary principles involved in the analysis of chemical processes with emphasis on material and energy balance calculations as applied to steady-state chemical systems. History of Chemical Engineering 1882 –a course in 'Chemical Technology' is offered at University College London. 1885 –a course in 'chemical engineering' is offered at Central College (later Imperial College), London. 1888 –a new curriculum at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) started: Course X, Chemical Engineering.
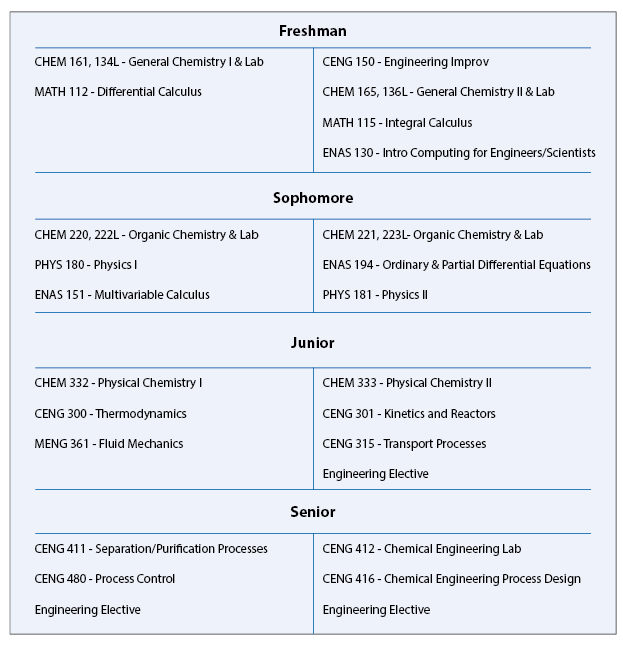
Bachelor of Science in Chemical Engineering
General Institute Requirements (GIRs)
The General Institute Requirements include a Communication Requirement that is integrated into both the HASS Requirement and the requirements of each major; see details below.
| Summary of Subject Requirements | Subjects |
|---|---|
| Science Requirement | 6 |
| Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences (HASS) Requirement; at least two of these subjects must be designated as communication-intensive (CI-H) to fulfill the Communication Requirement. | 8 |
| Restricted Electives in Science and Technology (REST) Requirement [can be satisfied from among 5.12, 5.07[J] or 7.05, 5.611/5.612, 10.301, and 18.03 in the Departmental Program] | 2 |
| Laboratory Requirement (12 units) [can be satisfied by 5.310] | 1 |
| Total GIR Subjects Required for SB Degree | 17 |
| Physical Education Requirement |
|---|
| Swimming requirement, plus four physical education courses for eight points. |
Departmental Program
Choose at least two subjects in the major that are designated as communication-intensive (CI-M) to fulfill the Communication Requirement.
| Required Subjects | Units | |
| Foundational Subjects | ||
| 5.12 | Organic Chemistry I | 12 |
| 5.310 | Laboratory Chemistry (CI-M) | 12 |
| 5.601 | Thermodynamics I | 6 |
| 10.10 | Introduction to Chemical Engineering | 12 |
| 18.03 | Differential Equations 1 | 12 |
| Intermediate Subjects | ||
| 10.213 | Chemical and Biological Engineering Thermodynamics | 12 |
| 10.301 | Fluid Mechanics | 12 |
| 10.302 | Transport Processes | 12 |
| Select one of the following: | 12 | |
| Principles of Inorganic Chemistry I | ||
| Introduction to Biological Chemistry | ||
| Organic Chemistry II | ||
5.611 & 5.612 | Introduction to Spectroscopy and Electronic Structure of Molecules | |
| General Biochemistry | ||
| Select one of the following: | 15 | |
| Chemical Engineering Projects Laboratory (CI-M) | ||
| Energy Engineering Projects Laboratory (CI-M) | ||
| Chemical-Biological Engineering Laboratory (CI-M) | ||
| Biological Engineering Projects Laboratory (CI-M) | ||
| Polymer Science Laboratory (CI-M) | ||
| Advanced Subjects | ||
| 10.32 | Separation Processes | 9 |
| 10.37 | Chemical Kinetics and Reactor Design | 12 |
| 10.490 | Integrated Chemical Engineering | 9 |
| Select one of the following:2,3 | 6 | |
| Integrated Chemical Engineering Topics I | ||
| Integrated Chemical Engineering Topics I | ||
| Integrated Chemical Engineering Topics II | ||
| Integrated Chemical Engineering Topics III | ||
| Integrated Chemical Engineering Topics III | ||
| Restricted Electives | ||
| Select 21-30 units of restricted electives, including one from each category below: | 21-30 | |
One subject of at least six units in Chemical Engineering2, 3 | ||
One subject of at least 9 units in Chemical Engineering3 | ||
One engineering laboratory subject of at least 6 units4 | ||
| Units in Major | 174-183 | |
| Unrestricted Electives | 48 | |
| Units in Major That Also Satisfy the GIRs | (36) | |
| Total Units Beyond the GIRs Required for SB Degree | 186-195 | |
Course Materials Che 31. Introduction To Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Solution Manual
The units for any subject that counts as one of the 17 GIR subjects cannot also be counted as units required beyond the GIRs.
Course Materialsche 31. Introduction To Chemical Engineering
| 1 | 18.032 Differential Equations is also an acceptable option. |
| 2 | May be satisfied with a second term of 10.492A, 10.492B, 10.493, 10.494A, 10.494B, or a second term of 10.490 Integrated Chemical Engineering (with permission of instructor). |
| 3 | Graduate subjects may not be used as restricted electives. In addition, the following undergraduate subjects may not be used as restricted electives: 10.04, 10.792[J], 10.806, 10.910 and 10.911 Independent Research Problem, 10.UR and 10.URG Undergraduate Research, and 10.THU. |
| 4 | Consult the Chemical Engineering Student Office for a list of acceptable subjects. |